OpenEDG
Certifications
OpenEDG is proud to offer professional certifications designed to provide industry recognition of a test candidate's knowledge, skills, and proficiency in the areas of computer literacy, programming, web development, security, network administration, and the Internet of Things.
Python Institute Certifications
The OpenEDG Python Institute certification programs are independent and vendor-neutral, and are delivered in cooperation with schools, school districts, colleges, and universities, as well as training companies and IT industry leaders, and are available through the OpenEDG Testing Service (TestNow™), OnVUE Online Proctoring, and a network of 5,000 accredited Pearson VUE testing centers.
The OpenEDG Python Institute has defined an independent global certification path for the Python programming language. The path consists of seven certification tracks:
- General-Purpose Programming (PCEP™, PCAP™, PCPP1™, and PCPP2™ exams)
- Data Science (PCED™ and PCAD™ exams)
- Testing (PCET™, PCAT™, and PCPT™ exams)
- Security (PCES™, and PCAS™ exams)
- Automation (PCEA™, and PCAA™ exams)
- Artificial Intelligence (PCEI™, and PCAI™ exams)
- Web Development (PCEW™, and PCAW™ exams)
Candidates can take certification exams at three competency levels: entry, associate, and professional.
General-Purpose
Programming Track


PCEP™ – Certified Entry-Level Python Programmer
Level: Entry
Delivery Channel: Edube Interactive (OpenEDG Testing Service)
Cost: USD 69
Language: English, Spanish, Portuguese, Polish, Japanese
General-Purpose
Programming Track


PCAP™ – Certified Associate Python Programmer
Level: Associate
Delivery Channel: Edube Interactive (OpenEDG Testing Service)
Cost: USD 295
Language: English, Spanish, Japanese
General-Purpose
Programming Track


PCPP1™ – Certified Professional Python Programmer 1
Level: Professional
Delivery Channel: Pearson VUE/OnVUE Online Proctoring
Cost: USD 295
Language: English
Data Science Track


PCED™ – Certified Entry-Level Data Analyst with Python
Level: Entry
Delivery Channel: Edube Interactive (OpenEDG Testing Service)
Cost: USD 69
Language: English, Spanish
Data Science Track


PCAD™ – Certified Associate Data Analyst with Python
Level: Associate
Delivery Channel: Edube Interactive (OpenEDG Testing Service)
Cost: USD 295
Language: English
Testing Track


PCET™ – Certified Entry-Level Tester with Python
Level: Entry
Delivery Channel: Edube Interactive (OpenEDG Testing Service)
Cost: USD 69
Language: English, Spanish
Testing Track


PCAT™ – Certified Associate Tester with Python
Level: Associate
Delivery Channel: Edube Interactive (OpenEDG Testing Service)
Cost: USD 195
Language: English
Security Track


PCES™ – Certified Entry-Level Security Specialist with Python
Level: Entry
Delivery Channel: Edube Interactive (OpenEDG Testing Service)
Cost: USD 69
Language: English
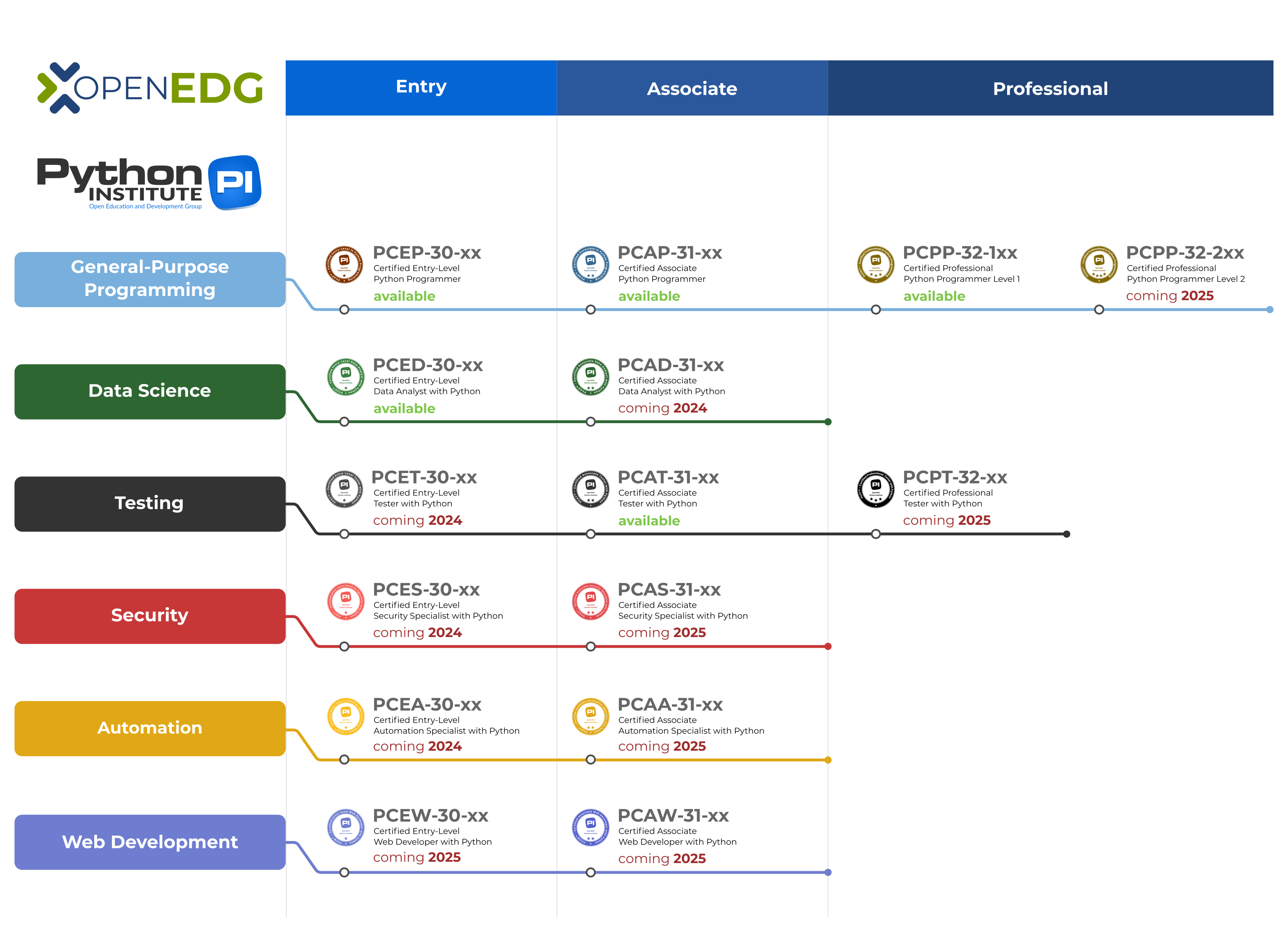
General-Purpose Programming

PCEP-30-0x
Certified Entry-Level Python Programmer

PCAP-31-0x
Certified Associate Python Programmer

PCPP1-32-10x
Certified Professional Python Programmer 1

PCPP2-32-20x
Certified Professional Python Programmer 2
Data Science

PCED-30-0x
Certified Entry-Level Data Analyst with Python

PCAD-31-0x
Certified Associate Data Analyst with Python
Testing

PCET-30-0x
Certified Entry-Level Tester with Python

PCAT-31-0x
Certified Associate Tester with Python

PCPT-32-0x
Certified Professional Tester with Python
Security

PCES-30-0x
Certified Entry-Level Security Specialist with Python

PCAS-31-0x
Certified Associate Security Specialist with Python
Automation

PCEA-30-0x
Certified Entry-Level Automation Specialist with Python

PCAA-31-0x
Certified Associate Automation Specialist with Python
Artificial Intelligence

PCEI-30-0x
Certified Entry-Level AI Specialist with Python

PCAI-31-0x
Certified Associate AI Specialist with Python
Web Development

PCEW-30-0x
Certified Entry-Level Web Developer with Python

PCAW-31-0x
Certified Associate Web Developer with Python
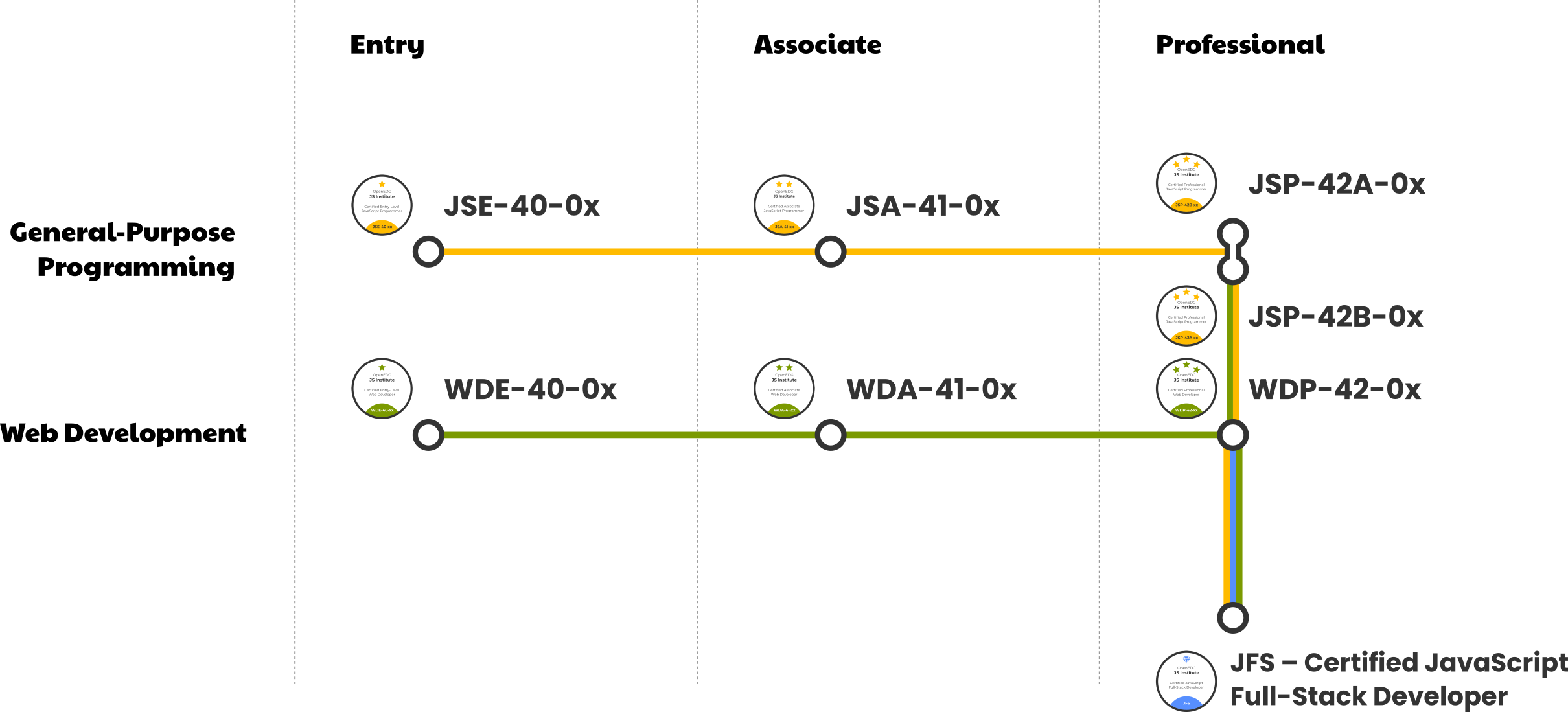
JS Institute Certifications
OpenEDG has defined an independent global certification pathway for the JavaScript programming language within the JS Institute certification program. The pathway consists of two certification tracks:
- General-Purpose Programming: JSE™, JSA™, JSPa™ (Client-Side Programming), and JSPb™ (Server-Side Programming) exams
- Web Development: WDE™ (HTML + CSS) and WDA™ (JavaScript + Node.js) exams)
Candidates can take certification exams at three competency levels: entry, associate, and professional.
General-Purpose
Programming Track


JSE™ – Certified Entry-Level JavaScript Programmer
Level: Entry
Delivery Channel: Edube Interactive (OpenEDG Testing Service)
Cost: USD 69
Language: English
General-Purpose
Programming Track


JSA™ – Certified Associate JavaScript Programmer
Level: Associate
Delivery Channel: Edube Interactive (OpenEDG Testing Service)
Cost: USD 295
Language: English
Web Development
Essentials Series


WDE™ – Certified Entry-Level Web Developer
Level: Entry
Delivery Channel: TestNow™
Cost: USD 69
Language: English
Web Development
Essentials Series


WDA™ – Certified Entry-Level Web Developer
Level: Associate
Delivery Channel: TestNow™
Cost: USD 125
Language: English
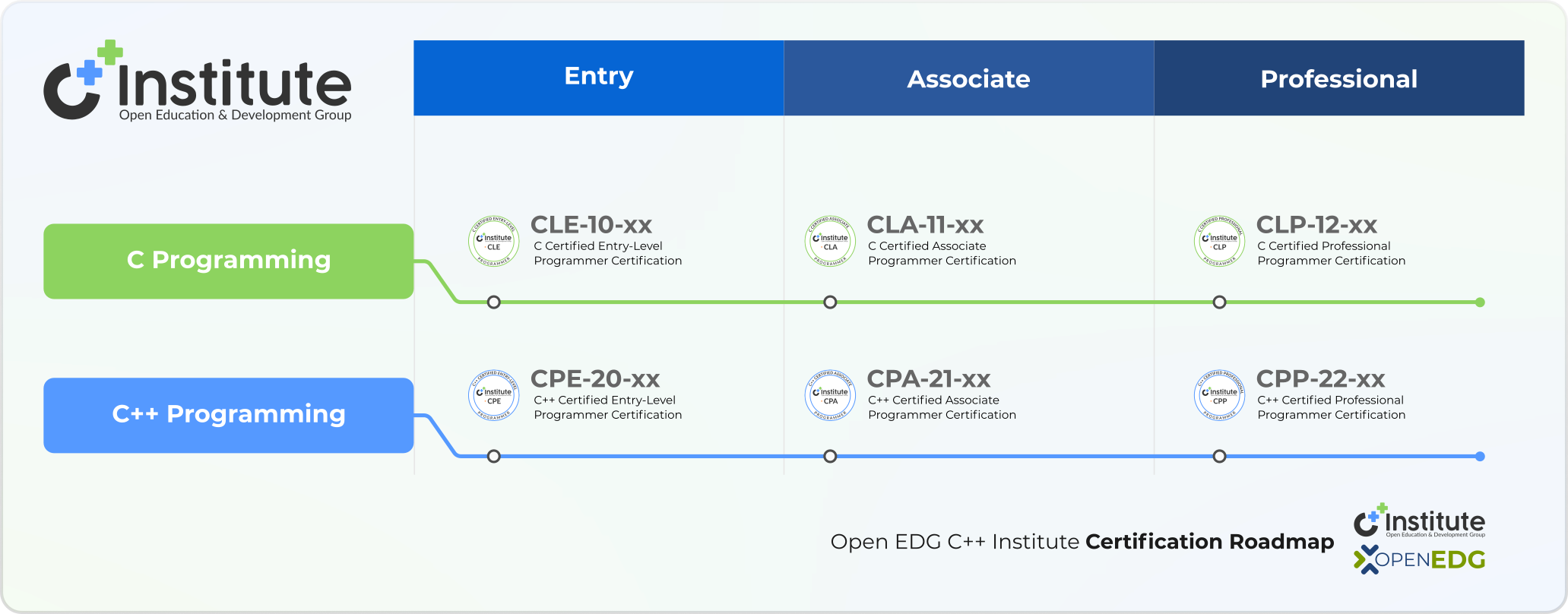
C++ Institute Certifications
OpenEDG has defined an independent global certification pathway for the C and C++ programming languages within the C++ Institute certification program. The pathway consists of two certification tracks:
- General-Purpose Programming in the C language: CLE™, CLA™, and CLP™ exams
- General-Purpose Programming in the C++ language: CPE™, CPA, and CPP™ exams
Candidates can take certification exams at three competency levels: entry, associate, and professional.
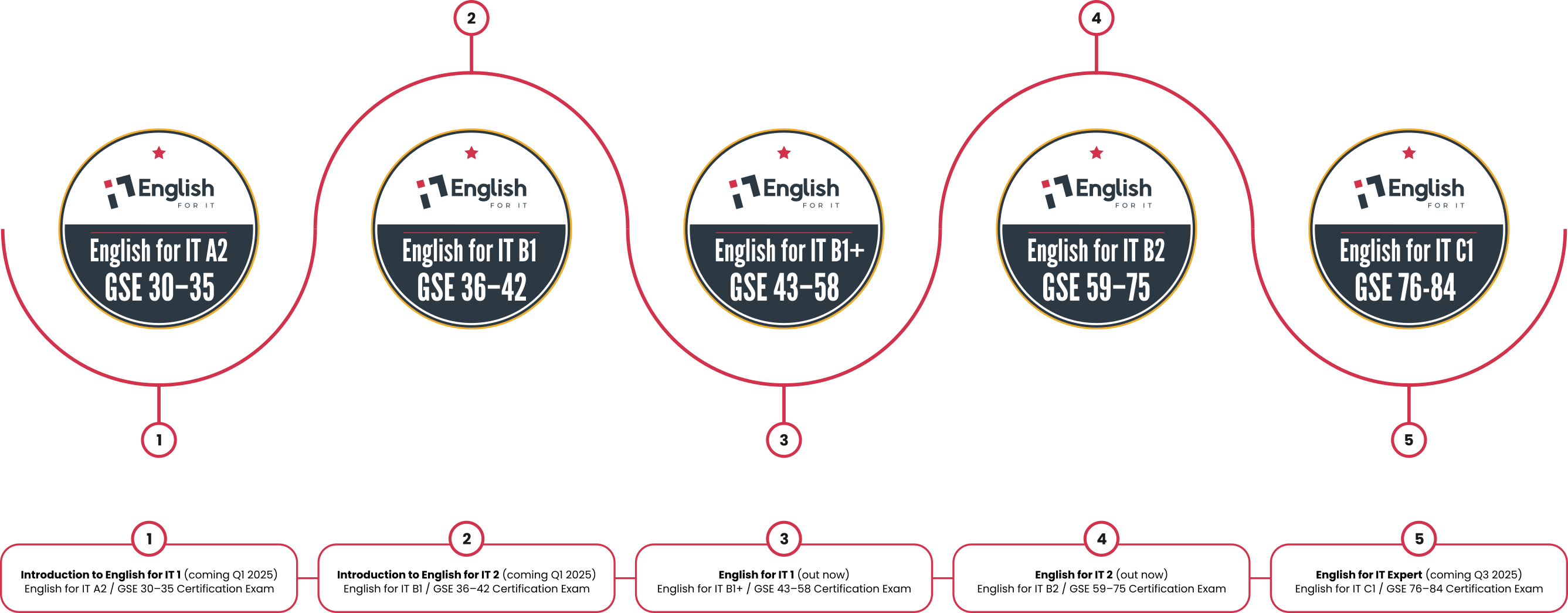
English for IT Certifications